个人作业
领域建模
阅读 Asg_RH 文档,按用例构建领域模型。
- 按 Task2 要求,请使用工具 UMLet,截图格式务必是 png 并控制尺寸。
- 说明:请不要受 PCMEF 层次结构影响。
你需要识别实体(E)和 中介实体(M,也称状态实体):
- 在单页面应用(如 vue)中,E 一般与数据库构建有关, M 一般与 store 模式有关。
- 在 java web 应用中,E 一般与数据库构建有关, M 一般与 session 有关。
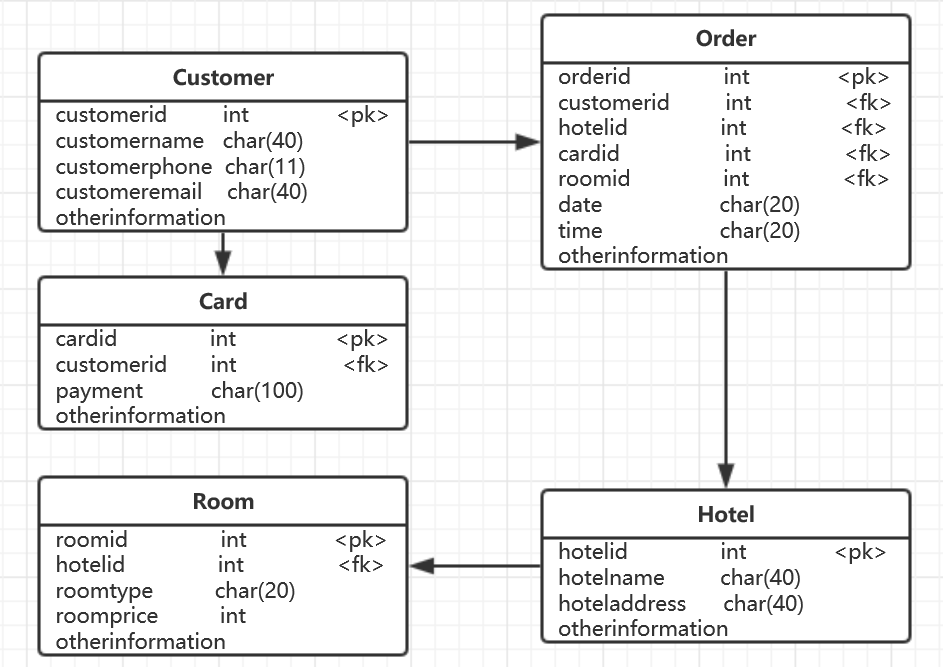
数据库建模(E-R 模型)。
- 按 Task 3 要求,给出系统的 E-R 模型(数据逻辑模型)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
|
drop table if exists Card;
drop table if exists Hotel;
drop table if exists Room;
drop table if exists Custmer;
drop table if exists Orders;
create table Card
(
cardid int not null,
customerid int not null,
payment longtext not null
primary key (cardid)
);
create table Hotel
(
hotelname longtext,
hoteladdress longtext,
hotelid int not null,
primary key (hotelid)
);
create table Room
(
hotelid int,
roomprice int,
roomtype longtext not null,
roomid int not null,
primary key (roomid)
);
create table Customer
(
customername longtext not null,
customerphone longtext not null,
customeremsil longblob not null,
customerid int,
primary key (customerid)
);
create table Orders
(
customerid int not null,
hotelid int not null,
roomid int not null,
date datetime,
time datetime,
orderid int,
primary key (orderid)
);
alter table Card add constraint FK_Reference_1 foreign key (customerid)
references customer (customerid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Room add constraint FK_Reference_2 foreign key (hotelid)
references Hotel (hotelid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Orders add constraint FK_Reference_1 foreign key (customerid)
references customer (customerid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Orders add constraint FK_Reference_2 foreign key (hotelid)
references Hotel (hotelid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Orders add constraint FK_Reference_3 foreign key (cardid)
references Card(cardid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Orders add constraint FK_Reference_4 foreign key (roomid)
references Room (roomid) on delete restrict on update restrict;
|
概念模型:就是在了解了用户的需求,用户的业务领域工作情况以后,经过分析和总结,提炼出来的用以描述用户业务需求的一些概念的东西。概念数据模型是最终用户对数据存储的看法,反映了最终用户综合性的信息需求,它以数据类的方式描述企业级的数据需求,数据类代表了在业务环境中自然聚集成的几个主要类别数据。 概念数据模型的内容包括重要的实体及实体之间的关系。在概念数据模型中不包括实体的属性,也不用定义实体的主键。这是概念数据模型和逻辑数据模型的主要区别。
概念数据模型的目标是统一业务概念,作为业务人员和技术人员之间沟通的桥梁,确定不同实体之间的最高层次的关系。
逻辑模型:就是要将概念模型具体化。要实现概念模型所描述的东西,需要那些具体的功能和处理那些具体的信息。这就到了需求分析的细化阶段。
物理数据模型是在逻辑数据模型的基础上,考虑各种具体的技术实现因素,进行数据库体系结构设计,真正实现数据在数据库中的存放。
物理数据模型的内容包括确定所有的表和列,定义外键用于确定表之间的关系,基于用户的需求可能进行发范式化等内容。在物理实现上的考虑,可能会导致物理数据模型和逻辑数据模型有较大的不同。
物理数据模型的目标是指定如何用数据库模式来实现逻辑数据模型,以及真正的保存数据。